Stem Cell-Based Therapy For Blindness: A Medical Eye-Opener
The Blind Spot
Advancements in modern medicine have paved the way for effective long-term eye disease remedies. Despite these innovations, we still have no reliable solution for restoring lost vision in patients, which makes treating eye disorders like glaucoma a significant challenge. Contemporary medical & pharma research is exploring the potential of stem cell treatment as a long-term solution for vision impairment.
Stem Cells: Biological Wildcards
In layman's terms, stem cells are the building blocks for the different tissues within our system. This includes the highly specialized cells situated in our eyes, such as rods and cones which enable our light and colour perception. The core goal of stem cell research in this field is to introduce and replace atrophied cells in the eye to restore vision loss due to various eye diseases. Sounds good on paper, but what about practical applications?
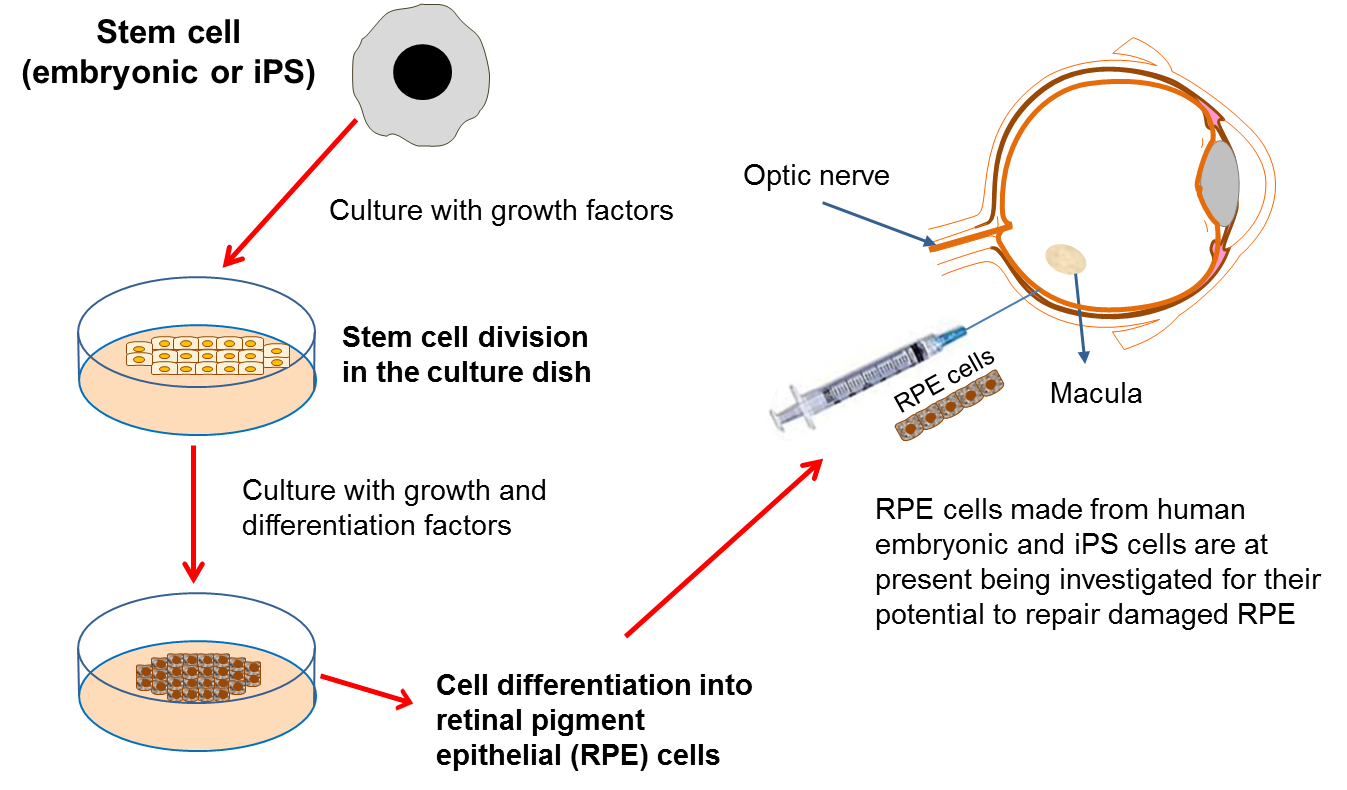
Regaining Vision
Let's take macular degeneration as an example. It's a common age-related eye disease that primarily affects one's central vision over time. Since it affects cells like photoreceptors in the eye, there is no known conventional cure for age-related macular degeneration.
Last year, however, a medical breakthrough in Boston saw a macular degeneration patient successfully regain lost vision after stem cell therapy. How does it work?
Stem Cells & Sight
Generally, DTS is caused by tear film dysfunction, the causes of which are as follows:
- The patient's retina is surgically detached for the procedure.
- Retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells sourced from stem cells are introduced into the retina.
- These RPE cells are instrumental in fixing the damaged photoreceptors in the retina, restoring vision and light perception in the process.
The success of this trial is merely the tip of the iceberg. Other eye ailments will require more specialized approaches, depending on the symptoms. However, with this successful trial, a world of possibilities for effective and safe eye treatment lies ahead.